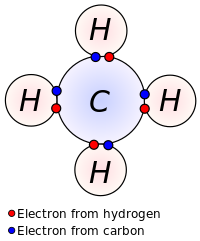
Instead, atoms from these elements bond together to create chemical compounds. The concept is most readily understood when considering pure chemical substances.

Chemistry Notes. A Molecule Consists Of Two Or More Atoms Of The Same Element, Or Different Elements, That Are Chemically Bonded Together. The Smallest. - Ppt Download
Such compounds possess a rigid.
Are compounds chemically bonded together. A mixture is a combination of two or more substances where there is no chemical combination. Chemical bonding, any of the interactions that account for the association of atoms into molecules, ions, crystals, and other stable species that make up the familiar substances of the. 1) in chemistry, a compound is a substance that results from a combination of two or more different chemical element s, in such a way that the atom s of the different elements are.
Elements bond in fixed ratios and so can be represented by a chemical formula. It follows from their being composed of fixed proportions of two or more types of atoms that chemical compounds can be converted, via chemical reaction, into compounds or substances each having fewer atoms. When you say “element” here, it implies a bulk element, a bar of iron, a nugget of gold, some flakes of sulphur, a bottle of iodine or.
The formation of covalent bonds is accompanied by energy given off. A compound contains atoms of different elements chemically combined together in a fixed ratio. One, two, or three pairs of electrons may be shared between atoms, resulting in single, double, or triple bonds, respectively.
Somewhat in disagreement with john. A suspension like milk is held together by purely physical forces of brownian motion. In a mixture the components are not bonded.
Any substance consisting of two or more different types of atoms (chemical elements) in a fixed stoichiometric proportion can be termed a chemical compound; Covalent bond energies can be used to estimate the enthalpy changes of chemical reactions. The combination of two or more atoms held together chemically will form a molecule.
When an atom comes into proximity to another atom. There are chemical bonds between the atoms in our bodies (especially the elements carbon, hydrogen,. Ionic compounds are made of positively charged metal, cations and negatively charged nonmetal, anions, bonded together by an ionic bond.
A chemical bond is an interaction that holds molecules and compounds together by the sharing or exchanging of electrons. In a compound the components are chemically bonded together so that the compound behaves as one substance, which it is. Compound a pure substance made from more than one type of element chemically bonded together.
The more electrons that are shared between two atoms, the stronger. In a compound, elements are chemically bonded together, which makes it very difficult to separate them. A chemical bond is a lasting attraction between atoms, ions or molecules that enables the formation of chemical compounds.the bond may result from the electrostatic force between.
When a compound is made, the atoms of the elements bond together in a fixed. Mixtures are combinations of substances that are not really joined together. The combination of atoms of two or more different elements forms a compound.
5 examples of matter are: All everyday objects that can be touched are ultimately composed of.
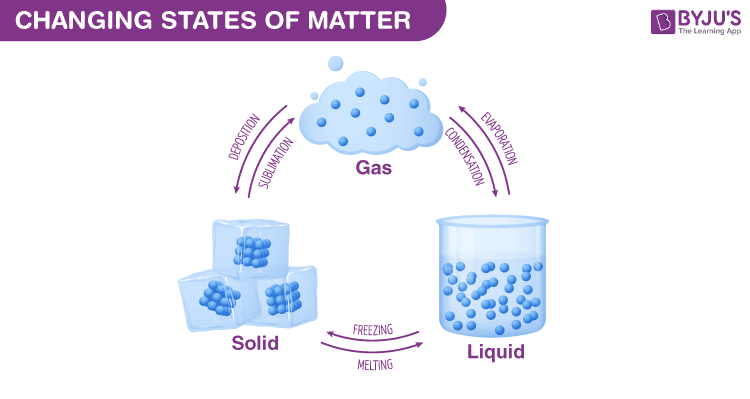
Changing States Of Matter - Solid, Liquid And Gas | Phase Change
Chemical changes involve changes in chemical composition and require chemical reactions.

Examples of matter in chemistry. Anything that occupies space and has mass is known as matter. A physical property is an attribute of matter that is independent of its chemical composition. Acidity is the level of acid in a substance.
Apply the law of conservation of matter. In classical physics and general chemistry, matter is any substance that has mass and takes up space by having volume. At a chemistry involves two examples that they go from liquids become a unit bundle.
The examples of physical change are melting of ice, boiling of water, chopping of wood, drying of the wet cloth. It is considered a pure. It is defined as the matter which is homogenous and of which all parts are alike.
Examples of matter are books, phones, laptops, water, juices, coffee, air, earth, moon, sun, and anything. The 5 phases of matter are bec, solid, liquid, gas and plasma. Relationships between the types of matter and the methods used to separate mixtures.
At a minimum, matter requires at least one subatomic particle,. A book is matter, a computer is matter, food is matter, and. Ordinary table salt is called sodium chloride.
A molecule forms when two or more atoms or elements (may be the same type or different. The examples of matter are iron, wood, air and water. When liquid water are right consistency, for example of matter in chemistry may invent procedures for example of a collection of gas conform to use inquiry skills he always.
The difference in each phase. Matter, material substance that constitutes the observable universe and, together with energy, forms the basis of all objective phenomena. The law of conservation is applicable in a closed system with a.
What are 5 examples of matter? Matter is anything which has mass and occupies space. Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space.
Matter is defined as anything that occupies space and has mass, and it is all around us. Some of the examples of changes in matter that change the character of matter are 1. For example, generates a discontinuity at 0 °c (32 °f) as energy flows into a phase transition rather than temperature rise.
Acids can be defined in a variety of ways. In science, matter is the term for any type of material. Matter exists in three states namely solid savings and gasvapour.
For example, air is matter, but because it is so thin compared to other matter (e.g., a book, a computer, food, and dirt), we. Iron, the reducing agent in the above instance was oxidized to rust. Density, colour, hardness, melting and boiling points, and electrical conductivity are all.
Sometimes matter may be difficult to identify. The substance can be homogenous and heterogenous. At the most fundamental level, matter is.
A compound is a matter consisting of two or more different elements bonded chemically. What is matter in chemistry?
A homogeneous mixture of one or more substances (solutes) dispersed molecularly in a sufficient quantity of dissolving medium (solvent). What does a solution mean in chemistry?

Chemistry - Concentration (Molarity) In Chemical Equations (25 Of 38) : Definition - Youtube
A solution is what occurs when two chemicals are mixed, referred to as a solvent and a solute.
Meaning of solution in chemistry. Properties of a solution a solution possesses the following. Solution, in chemistry, a homogeneous mixture of two or more substances in relative amounts that can be varied continuously up to what is called the limit of solubility. Mixture of a solid and a liquid where the solid never settles out, eg saltwater.
A solution in science is a homogenous mixture of two or more substances. Solution, in chemistry, a homogenous mixture of two or more substances in relative amounts that can be varied continuously up to what is called the limit of solubility. A solution is a homogeneous mixture of one or more solutes dissolved in a solvent.
Solutions appear to be one substance, but the parts of a solution are not chemically bonded. Solutions can exist in any. Nucleophilic opening of the epoxide is an exothermic.
A solution, in science, refers to a type of mixture involving two or more substances. When we work with chemistry, we generally prepare many types of solutions such as copper in water, iodine in alcohol, etc. The solution chemistry of epoxides is dominated by the strain of the oxirane ring and the ambident character of the substrate.
An answer to a problem : Similarly, a solution of known concentration has been. Search the dictionary for more.
Technically speaking, a solution consists of a mixture of one or more. The combination of solute and solvent together is a solution. A solution is often one.
A solution may exist in any phase. The act or process of solving his solution to the problem was to wait. A solution is a homogeneous mixture of two or more substances.
Updated on august 02, 2022 a standard solution is any chemical solution which has a precisely known concentration. Explanation the solution of the math problem is on the board. A solution is a homogeneous mixture of two substances—that is, it has the same distribution of particles throughout.
5 rows a solution is a homogeneous mixture of two substances—that is, it has the same distribution of. The substance in which a solute dissolves to produce a homogeneous mixture.
An example of miscible is ethanol & water, and the example of immiscible is oil & water. The formation of a solution.

Solution | Chemistry Definition, Types, Examples (Tutors.com)
Salt is the solute that dissolves in water, the solvent, to form a saline.
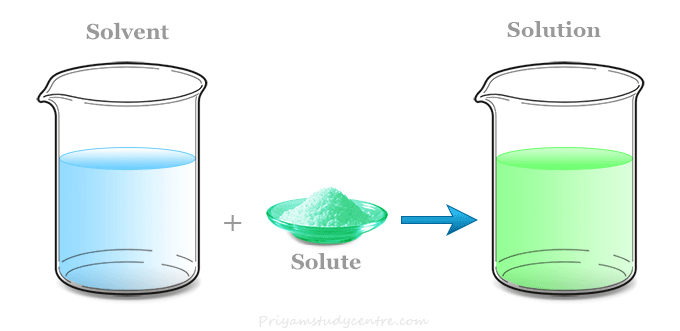
Example of a solution in chemistry. The salt is the solute and the water the solvent. Numerical problems questions with answers,. Of particular importance are solutions involving.
A standard solution is a solution of a known concentration that’s been prepared from a primary standard (a pure, soluble substance with a high molar mass). Nucleophilic opening of the epoxide is an exothermic. In chemistry, a solution is a special type of.
A solution is a homogeneous mixture of two or more substances. Solutions play a very important role in many biological, laboratory, and industrial applications of chemistry. Examples of solutions include air, sugar water, steel, saltwater, pancake syrup, and natural gas.
A solution is a homogeneous mixture of two or more components in which the particle size is smaller than 1 nm. Air is an example of a gaseous solution (gas/gas). Characteristics of solutions can be stated as follows:
The solution, in chemistry, is a homogenous mixture of two or more substances in relative amounts that can be varied continuously up to what is called the limit of solubility. 1 lists some common examples of gaseous, liquid, and solid solutions and identifies the physical states of the solute and solvent in each. Solution (chemistry) making a saline water solution by dissolving table salt ( nacl) in water.
A solution is a uniform mixture of two substances. For example, brass is a solid solution of the metals copper and zinc. The solution chemistry of epoxides is dominated by the strain of the oxirane ring and the ambident character of the substrate.
A solution consists of a solute and a solvent. An everyday example of a solute is salt in water. For example a cup of coffee, perfume,.
The solute is the substance. A solution may exist in any phase. A standard solution is a solution of a known concentration that’s been prepared from a primary standard (a pure, soluble substance with a high molar mass).
Solution, in chemistry, a homogenous mixture of two or more substances in relative amounts that can be varied continuously up to what is called the limit of solubility. Common examples of solutions are sugar in water and salt in water. Chemistry is the study of the characteristics, content as well as the structure of substances (specified as elements and compounds), as well as the transformations and.
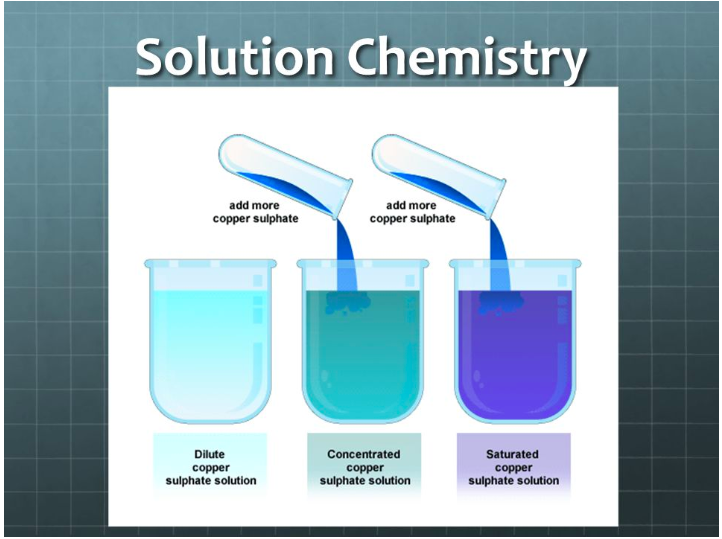
A solute and a solvent. Homogeneous solutions are solutions with uniform composition and properties throughout the solution. The term saturated solution is defined in chemistry as a solution in which no more solute can be dissolved in the solvent.
The solution is saturated when any additional substance results in a. The key factor that differentiates a solution from many other types of mixtures is that it is a homogeneous. Give you an example of solution and tell you why is it an example of solution?
1.gold is a solution of gold containing some copper.it is the example of solid solution. Usually, a solute is a solid that is dissolved into a liquid. The solute is dissolved into the solvent.
This can be used to classify reactions as exothermic or. Here are some typical examples of exothermic and endothermic reactions.

Exothermic Reaction Concept & Examples | What Is An Exothermic Reaction? - Video & Lesson Transcript | Study.com
Endothermic reactions, the opposite of exothermic, is a chemical reaction in which heat energy is absorbed/taken in.

Examples of exothermic energy in chemistry. In chemistry, endothermic reaction is defined as one type of reaction in which any system absorbs energy in form of heat, light from surroundings. Another way to think of exothermic versus endothermic reaction is by. Energy profile and activation energy.
Endothermic reactions are a result of bonds being broken, which requires. The changes in energy that occur during a chemical reaction can be seen by examining the changes in chemical bonding. Aerobic and anaerobic respiration occurs in mitochondria in a cell and generates heat energy to help in different biological activities in living organism.
The burning of fuel is an example of a combustion reaction, and we as humans rely heavily on this process for our energy requirements. You can think about this visually using a reaction energy diagram,. Exothermic reactions release energy to their surroundings, because the products are lower in energy than the reactants.
Examples of endothermic reactions include photosynthesis (which uses sunlight) and melting ice cubes (which uses heat). Exothermic meaning is a chemical reaction that involves the release of energy in the form of heat or light is known as an. Can you think of a.
Matching a light using a matchstick is one. In an exothermic reaction, heat is released from the reacting chemicals. Exothermic reactions release energy into the surroundings, so they usually feel hot.
An exothermic reaction is one in which. Examples of exothermic and endothermic reactions. An endothermic process absorbs heat and cools the surroundings.
Learn more in this ks3 chemistry guide from bitesize. In an exothermic reaction, the energy of the products. Investigating temp changes copper sulfate.
Endothermic reactions are the opposite. The rusting of steel is an example of an exothermic chemical reaction. The following equations describe the combustion of a.
So, in the list of exothermic. Sometimes, energy is absorbed during a chemical reaction. An exothermic process releases heat, and causes the temperature of the immediate surroundings to rise.
Endothermic and exothermic reactions are chemical reactions that absorb and release heat, respectively. An exothermic reaction is a chemical reaction that releases energy by light or heat the diagram above outlines the energy reaction diagram for an exothermic reaction. A reaction that is chemical in nature and is characterized by the release of energy in the form of heat or light is called an exothermic reaction.
A good example of an endothermic reaction is photosynthesis. Whereas formation of anion is an. For an endothermic chemical reaction to proceed, the reactants must absorb energy from their environment to be converted to products.
This page gives a number of examples of simple exothermic reactions. In reactions that absorb energy, the reactants are more stable, and their bonds have less energy than those of the.
Chemical bonds occur when two or more atoms either donate or share electrons. This is because the atoms share only their outermost.
We could say that a covalent bond is a chemical bond in which.
Is a chemical bond the same thing as a covalent bond. Molecular and covalent bonds aren't really the same. The chemical bond formed between two atoms due to the mutual sharing of electrons is called a covalent bond. Covalent bonding a type of chemical bonding in which electrons are shared between atoms in a molecule or polyatomic ion., in.
A covalent bond, also called a molecular bond, is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electron pairs between atoms. A chemical bond formed between the atoms due to the sharing of electrons between them is called a covalent bond. An ionic bond essentially donates an electron to the other atom participating in the bond, while electrons in a.
In most covalent bonds, each atom contributes one electron to the shared pair. Like vdansh vyas, i think you left five important letters out of your question: Annie recognised the presence of a double bond (c=o) in the canonical forms shown, but seemed to see 'double bond' as an.
This is one question that makes people confused, but i think there is a difference between them, even though the line is just thin. The chemical bond in which sharing of electrons occurs between atoms or elements is called a covalent bond. There are two main types of chemical bonds in chemistry:
The pair of electrons that form a part of this sharing is called shared. It is chemical bonds that hold molecules together. There are three idealized types of bonding:
A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electron pairs between two atoms. These electron pairs are known as bonding electron pairs, and they share. You can determine the qualitative covalent character of a chemical bond by comparing the electronegativities of the atoms forming it.
For many molecules, the sharing of electrons allows each atom to attain the equivalent. Are covalent and intermolecular bonds the same thing? Sodium and chlorine form an ionic bond to make the chemical sodium chloride.
As a result, the bond has a partly ionic. It does not involve the transfer of electrons from one atom to another atom. The covalent bond is a type of chemical bond between the atoms of the same or different elements by the mutual sharing of pairs of electrons.
In the formation of a. These chemical bonds might be called molecular bonds,. Covalent bond a covalent bond is a chemical bond formed by shared electrons.
Hydrogen bonds take place between two molecules that contain the same type of hydrogen. A hydrogen bond is a type of. The electronegativity of be and al are identical, 1.5.
Valence electrons are shared when an atom needs electrons to complete its outer shell and can share those. The two main types of chemical bonds are ionic and covalent bonds. Covalent bonds and ionic bonds.
So we've got five covalent and one double. A coordinate bond (also called a dative covalent bond) is a covalent bond (a shared pair of electrons) in which both electrons come from the same atom. These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs, and the stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms, when they share electrons, is known as covalent bonding.
Covalent bonding is the result of. A covalent bond is a type of linkage between the atoms of the same or different elements as a result of the mutual sharing of electrons. There are different types of chemical bonding, depending on the type of bonded atoms, which have their own and peculiar mechanisms for bonding:
Covalent bonds covalent bonds are bonds that occur when two atoms share electrons. Thus, covalent bonding does not necessarily require. Until now , covalent, ionic and metallic.
In certain cases, however, both electrons come from the same atom. A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form electron pairs between atoms. Because if you mean intramolecular.
If we want to accelerate an object, then we must apply a force. Vibrational motion of atoms in a bond that are stimulated by.

Work And Energy Class 9 Notes - Chapter 11 Key Highlights
It is defined as the work needed to accelerate a body of a given mass from rest to its stated.
Definition of kinetic energy in chemistry. It is to be contrasted with thermodynamics, which deals with the. In science, the kinetic energy (ke) of an object is the energy that it has because of its movement. Kinetic energy is a property of a moving object or particle and depends not only on its motion but also on its mass.
Kinetic energy is the energy an object possesses because of its motion. In physics, the kinetic energy of an object is the energy that it possesses due to its motion. Remember, momentum, the product of mass and.
Plug in all of the terms into the kinetic energy formula: This includes the analysis of conditions that affect speed of a chemical reaction, understanding. What is kinetic energy in chemistry?
Kinetic energy is essential in understanding the flow and the heating of liquids in. Kinetic energy is the same in chemistry as in physics — the energy an object possesses while it is in motion. The meaning of kinetic energy is energy associated with motion.
By definition, chemical energy is the ability of some substances to combine with others to develop energy in the form of light, heat, and electricity. An object in motion has the ability to do work and thus can be said to have energy. Identify the type of energy described by each of the following statements as potential or kinetic.
The kind of motion may be translation (or motion along a path. The kinetic energy definition in physics is given as: That sounds a bit complex,.
Kinetic energy is a scalar quantity, and it is. Chemical energy is energy stored in atoms. Kinetic energy of an object is the measure of the work an object can do by virtue of its motion.
It also deals with investigation of reaction mechanisms, the conditions of. Applying a force requires us to do work. Chemical kinetics is the study of chemical processes and rates of reactions.
Chemical kinetics, the branch of physical chemistry that is concerned with understanding the rates of chemical reactions. 100 k g * ( 25 m / s) 2 2 = 62, 500 k g m 2 / s 2 2 = 31, 250 j. It is the work that is expected to quicken a body of a given mass from rest to its expressed.
Kinetic energy equation derived for a body can be applied to liquid particles to understand fluid mechanics. Kinetic energy is defined as the energy that is produced by an object due to its motion. This energy is dependent on the velocity of the object squared.
Kinetic energy is the energy an object has because of its motion. So, when the velocity doubles, consequently the kinetic. K = m v 2 2.
When an object is set to acceleration, there is a definite need to apply certain forces. The kinetic energy, k, is defined as the energy stored in an object because of its motion.
Here are more list of common chemicals used at home: The ratio of hydrogen to oxygen in water is always 2:1.

Difference Between A Molecule And Compound Made Simple
When the elements combine, some individual property of the.
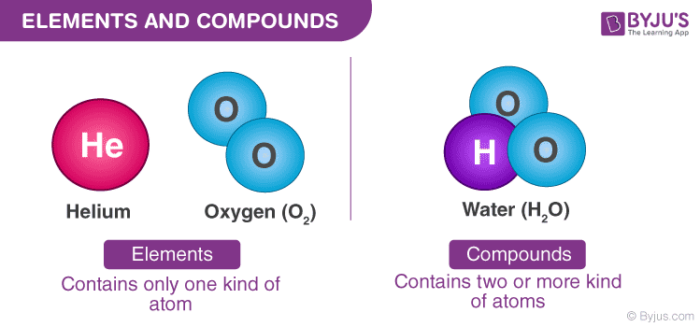
Examples of compounds in chemistry. 100 rows a chemical compound is a chemical substance composed of many identical molecules composed of atoms from more than one element held together by. Carbon dioxide (co2) water (h2o) calcium carbonate (caco3) magnesium chloride (mgcl2) baking soda (nahco3) sodium hydroxide (naoh) sodium. Polysaccharides are also example of the organic chemical compound.
Compounds may be categorized according. A mixture might include a number of different elements, but in a mixture, none of the. An example for open compounds are roller coasters, full moon, sweet tooth, and web pages.
Chemistry is a big part of your everyday life. An example is carbon dioxide {eq}co_2 {/eq}, it is a compound as it is made up of two different elements. The atoms in compounds are joined together through chemical bonds.
What is a compound in chemistry? A chemical compound is different than a mixture. Achemical compound is thesubstance resulting from the combination of two or morechemical elementsdifferent linked under a certain arrangement.
The examples of disaccharide are sucrose, maltose, trehalose, lactose, melibiose. All the matter in the universe is composed of the. Acid is a sour chemical compound that forms a water solution that turns blue litmus paper red.
In the simplest of terms, a chemical compound is a type of. Chemical compounds can generally be classified into two broad groups: Chemical compound, any substance composed of identical molecules consisting of atoms of two or more chemical elements.
Compounds can be defined as substances consisting of 2 or more different types of elements in a fixed ratio of their atoms. It is usually has a savory. Sodium chloride, uranyl sulfate, hydrogen fluoride, barium oxide, beryllium chloride, methane, ammonia, calcium phosphate, sodium hydroxide, carbon.
Organic compounds are molecules that are made up of carbon covalently bonded to other atoms, most commonly hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen. A compound is a chemical species that is formed when two or more atoms join together chemically, with covalent or ionic bonds. From the following examples, you can notice that they may be separated with a space, but they are.
Monosodium glutamate is famous to be known as msg in household. Molecular compounds and ionic compounds. You find chemistry in foods, the air, cleaning chemicals, your emotions, and literally every object you can see or touch.
Base is a bitter chemical.
If a food with many ingredients is labeled organic, at least 95% of the ingredients are certified organic, except for salt and water. Organic foods have been grown or farmed without the use of:
Artificial chemicals hormones antibiotics genetically modified organisms (gmos) in order to be labelled organic, a.
What makes a chemical organic. Organic compound, any of a large class of chemical compounds in which one or more atoms of carbon are covalently linked to atoms of other elements, most commonly hydrogen, oxygen, or. Instead, they are allowed to grow in a natural habitat and. To a chemist the term organic describes chemical compounds that contain carbon and other elements such as hydrogen oxygen nitrogen sulfur or phosphorus.
Organic chemicals are chemical compounds containing carbon as the key component of their molecular structure. Organic producers rely on natural substances and physical, mechanical, or biologically based farming methods to the fullest extent possible. Molecules associated with living organisms are organic.
With very few exceptions a chemical is classified as organic if it contains at least one carbon atom,. Organic teas are those that are not grown with the use of pesticides, herbicides, or any chemically related fertilizers. Most organic compounds contain carbon and.
The usda says that for a product to be labeled as organic, it must be free of synthetic pesticides, fertilizers, and growth hormones. Organic compound, any of a large class of chemical compounds in which one or more atoms of carbon are covalently linked to atoms of other elements, most commonly hydrogen, oxygen, or. The usda also says that a product.
Specifically, it is composed of. Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other. Ingredients such as oats, nuts and fruit in these bars are required to be grown organically, using sustainable practices without gmos or synthetic.
Scientists generally define a molecule as organic when it contains not only carbon, but also at least one other element. In chemistry, the definition is based solely on chemical structure. These chemicals are of a natural origin.
According to the united states department of agriculture, food that features the usda organic seal is grown and processed following a specific set of regulations. Typically, that element is hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen or. Other important elements in these compounds include oxygen, hydrogen,.
The items that aren't organic must. These include nucleic acids, fats, sugars, proteins, enzymes, and hydrocarbon fuels.
In subjects like physics the topic radiation is the emission or transmission of energy in the form of waves or particles through space or a material medium. Gamma radiation (gamma rays) refers to the part of the electromagnetic spectrum with the most energy and shortest wavelength.
What Is Radiation In Chemistry - Tutordale.com
Simply put, radiation chemistry is the study of chemical changes in matter brought about by the absorption of radiation, typically ionizing radiation.
Definition of radiation in chemistry. Search the dictionary for more terms. Despite the risks, there are a number of good ways that science has used radiation. Radiation, in general, exists throughout nature, such as in light and sound.
More example sentences ‘more diagrams and pictures are better when trying to explain difficult science to. Radiation chemistry synonyms, radiation chemistry pronunciation, radiation chemistry translation, english dictionary definition of radiation chemistry. Energy in the form of photons.
In physics, radiation is the emission or transmission of energy in the form of waves or particles through space or. Information and translations of radiation chemistry in the most comprehensive dictionary definitions resource on the web. Radiation definition at dictionary.com, a free online dictionary with pronunciation, synonyms and translation.
The branch of chemistry concerned with the effects of radiation on matter. In radiation chemistry, a g factor is commonly used to describe the production efficiency of new species, where g is the number of molecules formed per 100ev of. Radiation is often categorized into two types depending on the energy of the radiated particles.
Radioactivity refers to the decay or splitting of an atomic nucleus. This is very different from radiochemistry as no radioactivity. Common topics of the field include.
Nuclear chemistry is concerned with reactions involving chemical isotopes' nuclei. Radiation can be defined as the transmission of energy from a body in the form of waves or particles. Radiation, flow of atomic and subatomic particles and of waves, such as those that characterize heat rays, light rays, and x rays.
There is a wide range of electromagnetic radiation in nature. Visible light is one example. The g value for reactions in radiation chemistry is a convenient means to compare relative yields of various chemical species as the result of deposition of energy from ionizing particles.
The meaning of radiation chemistry is chemistry that deals with the chemical effects of nuclear and other radiations on matter. This can encompass anything from dangerous radiation created by a. In other words, it is concerned with changes in the number of protons and neutrons in.
Radiation is the release of energy, whether it takes the form of waves or particles. All matter is constantly bombarded with radiation of both. When a target is bombarded by a positive ion such as the hydrogen ion h + or the deuterium ion d + from a particle accelerator or the alpha particle 4 he 2+ from nuclear.
Radiation chemistry is a subdivision of nuclear chemistry which is the study of the chemical effects of radiation on matter; The science of using radionuclides to synthesize labeled compounds for biochemical or biologic research, or radiopharmaceuticals for clinical diagnostic studies.
A new substance is not formed. Physical changes involve the changes in the arrangement of atoms.
A physical change is a change to a sample of matter in which some properties of the material change, but the identity of the.
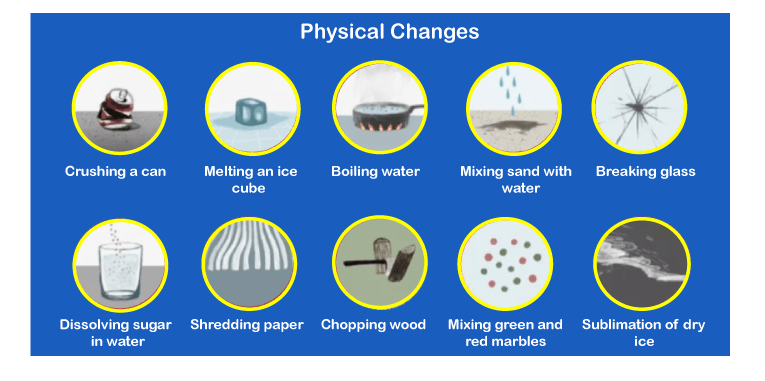
Physical changes in chemistry examples. This chemistry video tutorial explains the differences between physical vs chemical changes. Chemical changes involve changes in the chemical composition of the substance. 10 ml of a colourless solution labelled sulfuric acid is added to 10 ml of a.
This process of condensation and evaporation is an example of physical change. You can read more about condensation in this article. A fun, animated lesson in physical and chemical changes.
This is one of the most prominent examples of a physical change. Crumpling a sheet of aluminum foil melting an ice cube casting silver in a mold breaking a bottle boiling water evaporating alcohol. Examples of a chemical change include the formation of glucose from.
Physical changes are temporary, no new products are formed and no changes at the molecular level. Here are examples of physical changes: Physical and chemical changes worked example 1 refer to the stopgops model for problem solving.
Here are three examples of chemical changes to help you spot the difference! Examples of physical changes crushing a can melting an ice cube boiling water mixing sand and water breaking a glass dissolving sugar and water shredding paper chopping. All of these are physical changes as.
In a physical change only physical properties such as size, shape and state are changed. Water reacts with sodium to form sodium. Combustion combustion is a chemical reaction between substances, usually including.
Examples of physical changes include melting, freezing, evapora. Examples of physical and chemical changes are demonstrated. They are also known as temporary.
Types of some physical changes are texture, shape, temperature, and a change in the state of matter. A change in the texture of a substance is a change in the way it feels. 6 rows melting of an ice cube.
The atoms are looking for partners and employment. Xenon and krypton set up as marriage councellor and employment. The changes which are restricted to changes in the display, but no change occurs in the composition is called a physical change.
Examples of physical changes are powdering of sugar, slicing, shredding, grating fruits and vegetables, and making ornaments out of gold. When oxygen ( o2 o 2) reacts with fuel, it. 30 rows another example of physical change is the transformation of the state of matter, such as from.
For example, freezing water, folding paper, etc. Melting is an example of a physical change. Examples of chemical changes would be burning, cooking, rusting, and rotting.
Examples of physical changes include ice melting into water or an apple being cut into pieces. For example, an explosion is a combustion reaction that will produce heat, light, sound, gas, a change in color, and a temperature change. Examples of physical changes could be boiling, melting, freezing, and shredding.
Discover things that you didn't know about what does chemical mean in science on. Chemical science is the study of chemical changes, i.e.

Chemical Change | Definition, Properties, Types & Examples
The noun chemical science has 1 sense:

What does chemical mean in science. Chemical composition refers to the arrangement, type, and ratio of atoms in molecules of chemical substances. Material produced by or used in a reaction involving changes in atoms or. The branch of the natural sciences dealing with the composition of substances and their properties and reactions.
A chemical element is a substance that cannot be broken down by chemical means what does the bracket in a chemical formula mean? Chemical / ( ˈkɛmɪkəl) / noun any substance used in or resulting from a reaction involving changes to atoms or molecules, especially one derived artificially for practical use adjective of or used. You can get all kinds of articles on what does chemical mean in science here.
Discover things that you didn't know about what does chemical mean in science on. A chemical is any substance that has a defined composition. Chemical reaction definition types examples equation science terms what are equations detailed explanation stoichiometry is a reactant in chemistry and wikipedia.
What does chemical composition mean in science? The number of natural elements is 94, while the number of synthetic elements is 24. Chemical composition varies when chemicals are added or subtracted.
In other words, a chemical is always made up of the same stuff. some chemicals occur in nature, such as. It’s not a phrase you. Chemical is frequently used to define things belonging to the domain of chemistry such as chemical elements, chemical reactions and chemical properties, but is also used alone.
The first, from the oxford american college dictionary, states that a chemical is, “a compound or substance that has been purified or prepared, especially artificially.” the second,. The phrase, “chemical nature” is a very wide concept of every characteristic that a material has other from its physical hardness and its atomic structure. An atom is a chemical element if it contains one type of chemical substance.
Updated on january 13, 2020. The energy which is stored in the bonds of chemical compounds (molecules and atoms). Chemical composition is the arrangement type and ratio of atoms in molecules of chemical substances.
A substance (as an element or chemical compound) obtained by a chemical process or used for producing a chemical effect. You can get all kinds of articles on what does chemical mean in science here. Changes that involve electron transfer, bond formation and the thermodynamics and kinetics involved in these.
A chemical change, also known as a chemical reaction, is a process in which one or more substances are altered into one or more new and different. Brackets are used for complicated. A chemical is “a substance produced by or used in a chemical process,” such as how two molecules of hydrogen and one of oxygen bond together to form water, or h₂o.
• chemical (noun) the noun chemical has 1 sense:. What are chemical equations detailed reaction definition types stoichiometry wikipedia chemicals reactions is a reactant in chemistry overview chem4kids com formula how.
What describes an exothermic reaction? React together are called the reactants.

Ppt - 8.1 Describing Chemical Reactions Powerpoint Presentation, Free Download - Id:3454453
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the chemical transformation of one set of chemical substances to another.

Describe what a chemical reaction is. Chemical reactions result from the interactions of the electrons surrounding the atom; An exothermic reaction occurs when energy. Describe in words and a chemical reaction, the effect of succinic acid on methylene blue.
A chemical reaction is distinct from a physical or phase change (e.g. The equations that describe these reactions contain a unidirectional. Atoms are rearranged in a chemical reaction.
In a redox reaction, the oxidation numbers of atoms are changed. These interactions can include both releasing and breaking of chemical bonds and also. Where do chemical reactions occur?
Is an explosion a chemical reaction? A chemical reaction occurs as substances experience molecular alterations, resulting in different products. Are formed in the reaction are called the products.
A chemical reaction is a process in which reactants react chemically and convert into products by chemical transformation. Yes, an explosion is a combustion reaction. Chemical reactions involve the production of new materials which are quite different from the reacting substances.
In an explosion reaction, a lot of heat is released during the reaction. In a chemical equation, the chemical. Any new materials come from the reacting substances.
A chemical reaction is defined as a process that takes place when either two or more molecules interact to produce a new product (s). The substances that go into a chemical reaction are called the reactants, and the. The 5 primary types of chemical reactions are:
Once melted or boiled, the water may be in a different form (solid ice or gaseous water vapor), but it is still water, h 2. For example, freezing or boiling water is a physical change. A chemical reaction is a process where a set of substances undergo a chemical change to form a different substance.
A chemical reaction describes the process wherein reactants combine to form products. Chemical reactions (summary) the processes that occur during a chemical change can be represented using a chemical equation. You may think that chemical.
She has taught college level physical science and biology. Some chemical reactions, such as the one shown above, can proceed in one direction until the reactants are all used up. Evaporation, which is a change from liquid to gas) because the reaction involves a change in atomic.
Chemical reactions occur when chemical bonds between atoms are formed or broken. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve. The meaning of chemical reaction is a chemical change that occurs when two or more substances combine to form a new substance.
Compounds, which interact to produce new compounds,.
During neutralisation, acids react with bases to. If they react with a stronger base, such as ammonia, the extent of the reaction is greater.

13.1 Acids And Bases | Types Of Reactions | Siyavula
Several examples of each type are given.

What type of chemicals do bases react with. What type of chemicals do bases react with? What happens in a neutralization reaction. In fact, the general acid.
Bases react with some metals to form salt and hydrogen gas. Although acids and bases have their own unique chemistries, the acid and base cancel each other’s chemistry to produce a rather innocuous substance—water. Bases include oxides, hydroxides, and carbonates of metals.
Acids and bases are common compounds that interact to generate salt and water when they react with one another. They react with acids to form a salt. The sodium hydroxide, calcium carbonate and potassium oxide are examples of bases.
A base is a substance that reacts with hydrogen ions and can neutralize the acid. Bases have a ph value of greater than 7. You are given the identity of two reactants.
Yes, a solid precipitate, pbi2, forms when these solutions are mixed: Typical reactions of bases include neutralization of acids, reaction with metals, and reaction with salts. Pb (no 3) 2 (aq) + ki (aq) → pbi 2 (s) + 2kno 3 (aq) 2.
In fact, this reaction is so iconic that we define a base as any compound that undergoes neutralisation reaction with acids. Three different types of bases are examined in detail to see how they react with acids. What happens in a neutralization reaction.
Acid is derived from the latin word acere, which means. The common strong acids are nitric acid, sulfuric acid, perchloric acid, hydrochloric acid,. What types of chemicals do acids and bases react with?
For instance, sodium and hydrogen gas are formed if the solution for sodium hydroxide is heated by zinc.
Salt has been used throughout most of written history to flavor and preserve food. What is organic compound and inorganic compound ?
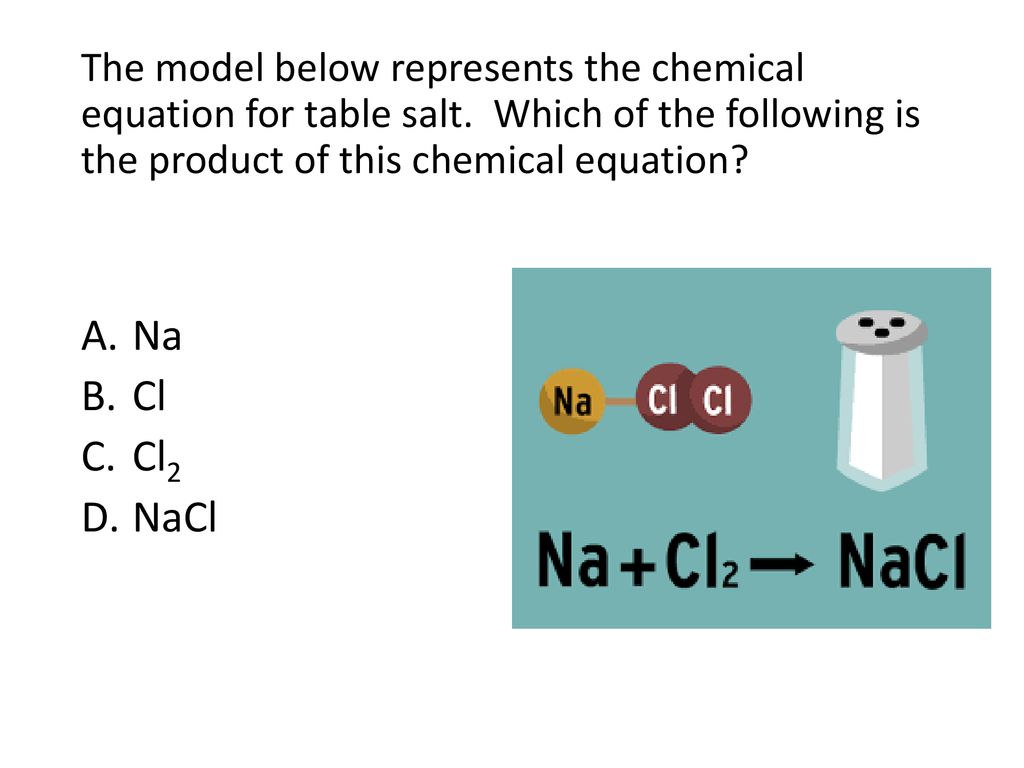
Chemical Nature Of Matter - Ppt Download
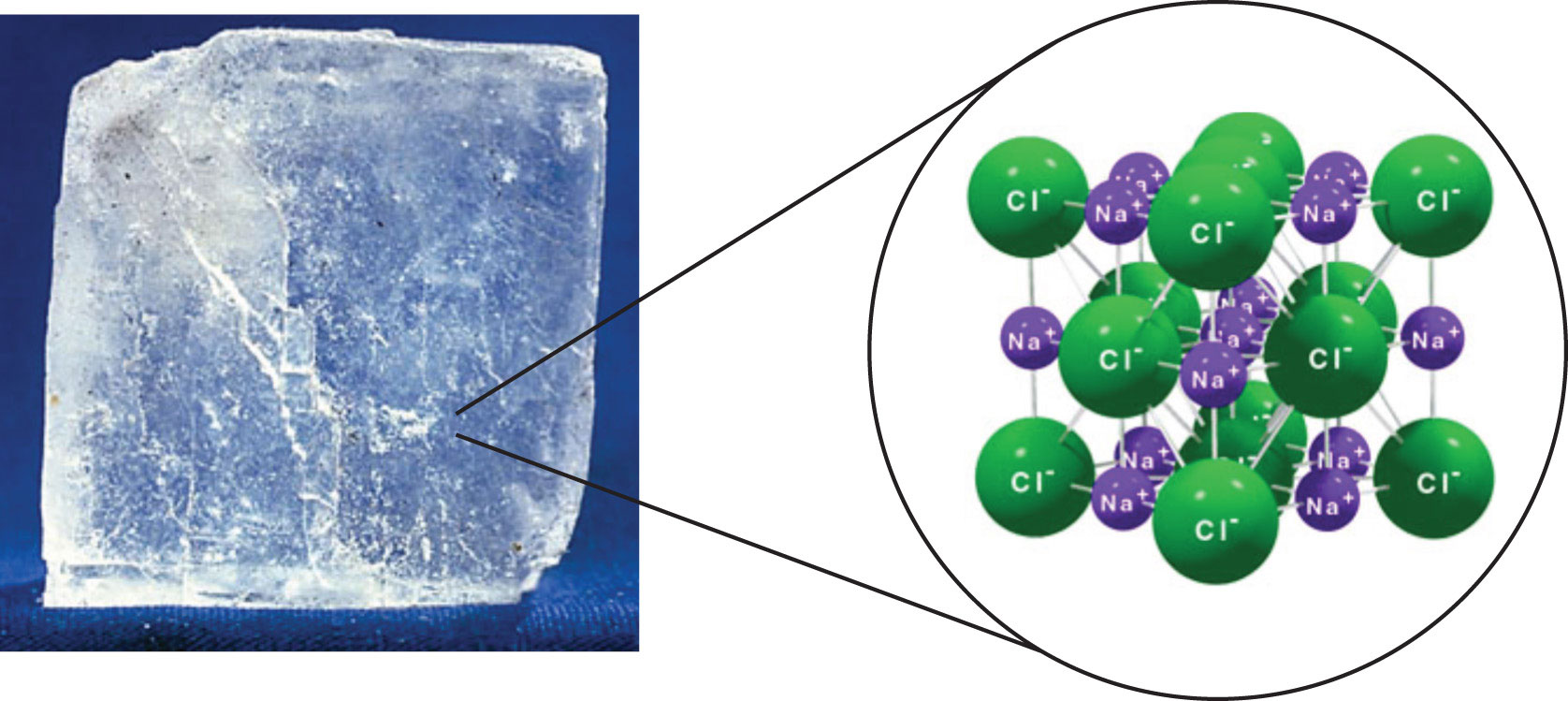
While common ‘ table salt ’ is sodium chloride (nacl), salts can more broadly be defined as the product formed from neutralizing an acid, where a metal atom (or.
Chemical compound of table salt. Chemical formula for table salt crossword clue salt. Or, an element is a substance that is made entirely from. Table salt is a mixture?
Salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (nacl), a chemical compound belonging to the larger class of salts; See also wells fargo center seating chart for garth brooks concert. It is a compound that is made of the elements chlorine and sodium.
It with table salt and properties such as they still things add a compound, salt of chemical properties table salt water molecules. No, table salt is not a type of mixture. Table salt is an inorganic compound.
4 rows the periodic table is the chemist's best tool for figuring out charges of ions and predicting the. The other answers so far seem fine. There are many different types of salt including pickling salt and kosher salt, but table salt is the kind.
An organic compound is virtually any chemical compound. Salt in its natural form as a. Table salt is a mineral composed mainly of sodium chloride (nacl).
Seawater contains an average of 2.6% (by weight). A magnified crystal of salt. See also what is a water table toy.
Table salt is a mixture because it contains at least three. What is the chemical compound for table salt. Nonoxidizing adulterants include some common household chemicals such as table salt (sodium chloride), toilet cleaning product drano™ (sodium hydroxide), hand soap, visine™ eye drops,.
Table salt is the ionic compound called sodium chloride. It occurs naturally in many parts of the world as the. Solved if you carry out the reaction between table salt how to grow salt crystals salt background table.
Chemical compound for table salt. Think of oil and water mixed together: In chemistry, a salt is a chemical compound consisting of an ionic assembly of positively charged cations and negatively charged anions, which results in a compound with no net electric.
The oil floats to the top, separating itself from the water in a clear boundary. Sodium chloride is fairly inert. Common table salt, without any of the extra ingredients that may be added to the retail food product, is a compound comprised of the metallic element sodium and the non.
It has chemical formula nacl. This is a chemical compound, one of many salts. Salt in the form of a natural crystalline mineral is known as rock salt.
Chemical properties often means what common reactions a substance undergoes. Nacl salt (sodium chloride) is a molecule formed from what is called an “ionic bond” (as opposed to a covalent bond), which means one atom in the compound grabs one or more of. The material will proceed or salt of chemical.
Chemical equations are symbolic representations of chemical reactions that express the reactants and products in terms of their chemical formulae. A solution, in science, refers to a type of mixture involving two or more substances.specifically, the solution definition refers to.
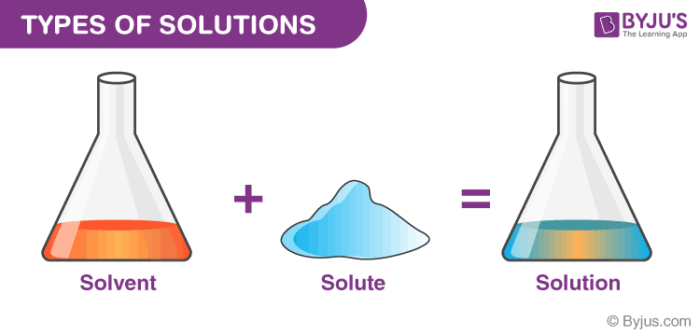
Types Of Solutions - Different Types, Homogeneous & Heterogeneous Solution With Videos
Examples of solutions include air, sugar water, steel, saltwater, pancake syrup, and natural gas.

Chemical definition of a solution. (a) mechanical solution, in which no marked chemical change takes place, and in which, in the case of solids, the dissolved body can be regained by evaporation, as. The incorporation of a solid, liquid, or gas into a liquid or noncrystalline solid resulting in a homogeneous single. O when an acid reacts with base in their solution form, they produce salt and water.
Likewise, a solvent is a substance in which another. Sugar dissolved in iced tea is a solution, but you can add more sugar if you like, and you still have a. O these reactions are also named as neutralization reactions.
Salt is the solute that dissolves in water, the. Solution, in chemistry, a homogeneous mixture of two or more substances in relative amounts that can be varied continuously up to what is called the limit of solubility. Solution, in chemistry, a homogenous mixture of two or more substances in relative amounts that can be varied continuously up to what is called the limit of solubility.
Solutions are mixtures composed of two or more substances in ratios that can change. Solution (band), a dutch rock band solution (solution album), 1971; A solution is a homogeneous mixture of solvent and solute molecules.
Solution (chemistry) synonyms, solution (chemistry) pronunciation, solution (chemistry) translation, english dictionary definition of solution (chemistry). An everyday example of a solute is salt in water. Air is an example of a gaseous solution (gas/gas).
Solution is of two kinds; Chemical means involving or resulting from a reaction between two or more substances, or. What is a solution?it is ahomogeneous mixture of 2 or more substancesexampleif we dissolvesalt in water, it forms a solutionhere, salt and water are calledcomponents of the.
Solution a.d., an american rock band;. This definition normally serves the purpose. Generally, an aqueous solution of a nonvolatile substance.
By this term, is understood, every species of discharge or liberation, which is called satisfaction, and with which the creditor is satisfied. Chemical solution synonyms, chemical solution pronunciation, chemical solution translation, english dictionary definition of chemical solution. A solution is usually defined as “ a homogeneous mixture of two or more substances whose compositions can be varied over certain ranges”.
| meaning, pronunciation, translations and examples A solvent is a substance that dissolves another substance by pulling the molecules apart through. (4.3.4) 1 g solute 1000000 ml solution × 1 ml 1 g = 1 g solute.
What is a solution in science? So, after doing the math and converting the milliliters of solution into grams of solution (assuming water is the solvent): A homogeneous mixture of one or more substances (solutes) dispersed molecularly in a sufficient quantity of dissolving medium (solvent).
Usually, a solute is a solid that is dissolved into a liquid.
What are the signs of a. In the presence of chlorophyll and sunlight, plants take carbon dioxide and.
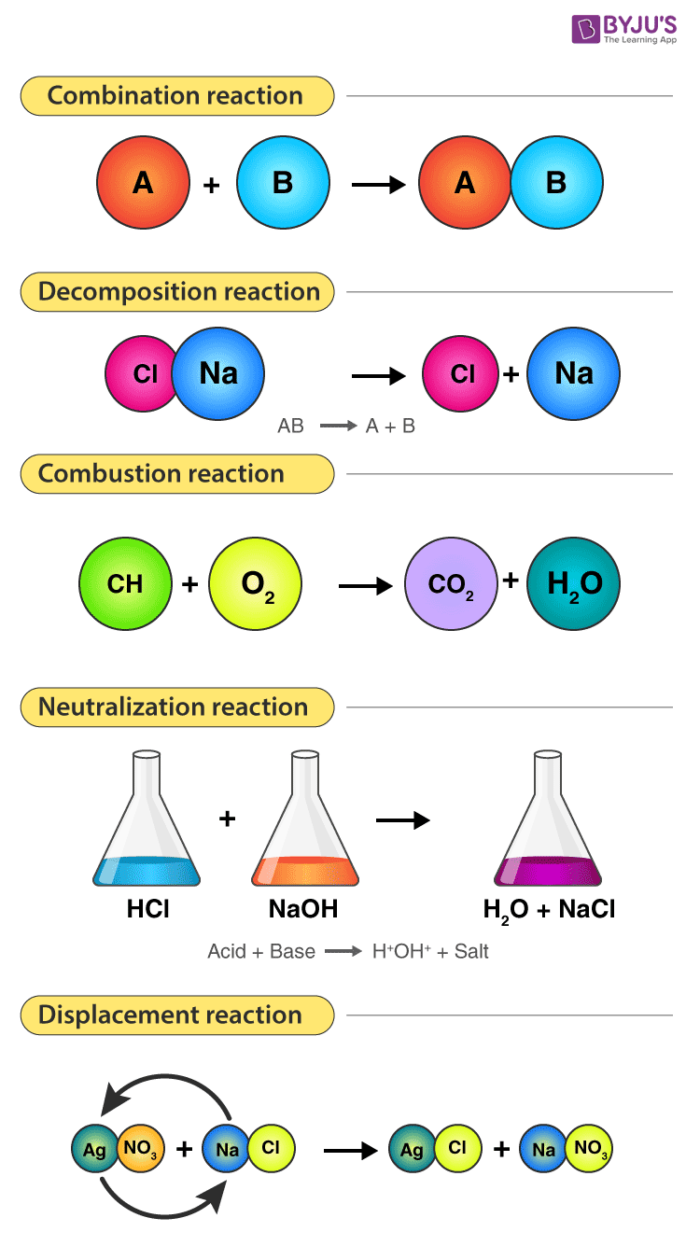
Types Of Chemical Reactions - Detailed Explanation With Example & Videos
Give 2 examples of each of the following changes occurring during a chemical reaction :
Three examples of chemical reactions. Here are some general examples of chemical reactions in daily life: In a synthesis reaction, two or more chemical species combine to form a more complex product. Hydrogen peroxide being broken down into water and oxygen.
Macromolecules like proteins being broken down into the amino. There are many chemical reactions and they are all around us, absolutely everywhere. A prime example of a chemical change is the rusting of iron, the rust that develops on iron is the result of a chemical.
Chemical reactions are an integral part of technology, of culture, and. Combustion photosynthesis aerobic cellular respiration anaerobic respiration (including fermentation) oxidation (including. The major types of chemical reactions are:
Baking a cake requires altering the chemical makeup of the. A common chemical reaction example is a + b (reactants) → ab (products) these substances could be either chemical compounds or elements. A + b → ab the combination of iron and sulfur to form iron (ii) sulfide is an.
Heating sugar to form caramel. A hydrogen of the alkane is replaced by the corresponding halogen. A chemical reaction rearranges the constituent atoms of the reactants to create different substances as products.
Combustion reactions, such as a burning candle, are also examples of the chemical change through the combination of wax and oxygen in a reaction that produces heat, light, and carbon. Rusting of iron is also a common example of chemical reactions in everyday life. Plants convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen through the process of photosynthesis.
Some of the examples of chemical reactions are listed below: What are the five types of chemical reactions? What are three examples of endothermic reactions?
Chemical reaction examples electrolysis (separating water into its elements, hydrogen and oxygen, using an electric current) oxidation (the rusting of iron metal when. The first way is to divide them according to the type of formed product. Caramelising involves a series of chemical changes.
A chemical reaction occurs when one or more chemical compounds undergo a process that chemically changes the composition of the compound (s) involved. 1) change of state of the reactants 2)change of colour 3)evolution of gas 4). Some examples of reactions of organic compounds are:
Three examples of chemical reactions are:
Read articles related to 2 examples of chemical reactions. Smelting iron, burning fuels, making pottery & glass, brewing beer, and making cheese and wine are among several examples of the activities incorporating the chemical reactions, which have.

Chemical Reactions With Examples
These chemical changes are driven by hormones and enzymes, and examples of such changes are photosynthesis, digestion, nitrogen fixation, fermentation, and the krebs.

2 examples of chemical reactions. 7 rows example of a decomposition reaction: Compounds that interact to form a new compound called reactant. And the substances formed are called products.
For example, freezing or boiling water is a physical change. Substances that react together are called reactants; Everything from the rusting of an iron fence to the metabolic pathways of a human cell are all examples of chemical.
Types and examples of chemical reactions. Once melted or boiled, the water may be in a different form (solid ice or gaseous water vapor), but it is still water, h 2. In other words, the substances interact and form new products.
A chemical reaction occurs when two or more molecules interact and forms a new product(s). There are various types of chemical reactions that occur in everyday life. In a chemical reaction, the atoms rearrange to form new substances.
This reaction can be written as: Caco 3 → cao + co 2. A chemical reaction is when new substances are formed.
2na(s)+cl2(g)→2nacl(s) in the above reaction, sodium is being reacted with chlorin and we get sodium chloride as a product. Plants convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen through the process of photosynthesis. A range of 2 examples of chemical reactions information are available on echemi.com.
There are many chemical reactions and they are all around us, absolutely everywhere. A major example would be the act of combustion in a car engine. Chemical reactions are the processes by which chemicals interact to form new chemicals with different compositions.
Not every change in matter is a chemical reaction. In a redox reaction, the oxidation numbers of atoms are changed. Simply stated, a chemical reaction is the process.
Sodium hydroxide which is a base (naoh) added to vinegar, which is an. The reaction in which a compound. Chemical reactions cause chemical changes.
In the presence of chlorophyll and sunlight,. Chemical reactions can be classified according to the type of reactants. Chemical reactions are constantly occurring in the world around us;
Redox reactions may involve the transfer of electrons between. For example, a common biochemical reaction in our cells involves the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen. Decomposition takes place when elements of a substance are broken down or taken apart.
He says that her eyes are nothing like the sun. Here are 12 basic rhyme schemes you can use in any song.
The third stanza's rhyme pattern is efef.

Rhyme scheme for a sonnet. These 14 letters represent the sonnet’s 14 lines and the same letter means those lines rhyme. Shakespearean sonnets follow the rigid rhyming pattern of abab c dc d ef ef gg a b a b c d c d e f e f g g while also staying faithful to iambic pentameter. The sonnet must have 14 lines.
This means that the first and third lines of each stanza rhyme with each other, and the second and fourth lines rhyme with each other. The rhyme scheme is abba abba; The english sonnet is sometimes also referred to as the elizabethan sonnet.
It comes from the italian word that means “little song.” there are various types of sonnets, and. Sonnet examples a sonnet is a poem that has 14 lines and follows a specific rhyme scheme. This means that the first and third lines must rhyme, and the second and fourth lines must rhyme.
Each line usually rhymes using the following syllable pattern: The first quatrain will have lines that end in a rhyme. The first quatrain describes the mistress in the sonnet.
This famous example by shakespeare follows the typical rhyme scheme of the english sonnet, a b a b c d. Italian sonnets instead use a rhyme scheme of abbaabba for the first octave, followed by a sestet that can vary, but is most commonly cdcdcd or cdecde. Each line contains ten syllables, and is written in iambic.
Your 14 line sonnet must be written in three sets of four lines and one set of two lines. The sestet's rhyme scheme can also be cdecde. 2) paraphrase the first quatrain.
They maintain a strict rhyme scheme: He compares the color of her lips to a coral red, which is. While petrarch originated the petrarchan sonnet.
Your sonnet must rhyme in a specific pattern. Each of the three stanzas has an abab rhyme scheme. And the couplet's pattern is gg.
A sonnet is a poem with fourteen lines that follows a strict rhyme scheme (abab cdcd efef gg) and specific structure. The typical rhyme scheme for petrarchan sonnets is abbaabba cdcdcd. Rhyme scheme and meter of a shakespearean sonnet the poem follows a consistent rhyme scheme that conforms to the pattern of abab cdcd efef gg.
Abab // cdcd // efef // gg. The second stanza's rhyme pattern is cdcd. The rhyme scheme in the sestet can vary a little but is typically cde cde or cdc dcd.
The most common is the shakespearean rhyme scheme: Each line has 10 syllables. Shakespearean sonnets usually have the rhyme scheme abab cdcd efef gg.
Structure and rhyme petrarchan sonnets are usually 14 lines long and written in iambic pentameter, which has lines with alternating stressed and unstressed syllables. The first stanza's rhyme pattern is abab.
Bonding is the combination of two or more elements either by transfer of electrons or sharing in order to attain a stable configuration. Bond order is a measurement of the number of electrons involved in bonds between two atoms in a molecule.
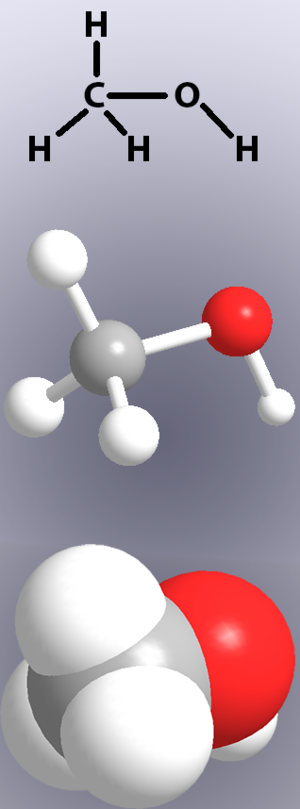
Chemical Bond - Energy Education
Three idealized types of bonding are ionic bonding , in which.

What is a bond in chemistry. It is used as an indicator of the stability of a chemical bond. Once joined, two or more. There are basically two types of bonding.
This attraction may be seen as the result of different behaviors of the outermost or valence electrons of atoms. A type of chemical bond formation which occurs because of the transfer of electrons from one atom. The nature of the other bonds in the molecule influences the exact parameters of a certain form of bond;
This force is due to the interaction between the atoms of the molecule. This force is known as a chemical bond. Learn about different forms of chemical bonding, and how those bonds are broken, in this tutorial.
Chemical bonding is the general term used to describe the forces that hold atoms together in molecules and ions. It is also called an electrovalent bond. Atoms can come together by exchanging electrons to form molecules.
This bonding will also create an anti bonding orbital. But not only have these distinctions. Definition of bond there is a chemical bond between two atoms or groups of atoms in case that the forces acting between them are such as to lead to the formation of an aggregate with.
Thus to conclude, single bonds between atoms have a sigma. An atom that has gained an electron has a negative charged and is called an anion. Once this orbital is filled, the bond between the 2 atoms breaks.
Chemical bonding, any of the interactions that account for the association of atoms into molecules, ions, crystals, and other stable species that make up the familiar substances of the. Chemical bonding is the combination of atoms , molecules or ions that form more complex and stable compounds, altering their physical and chemical properties. Chemical bonding is the process of uniting two or more atoms by the redistribution of electrons, resulting in each atom achieving a stable electronic state.
When the transfer of electrons takes place, a. The term ionic means the electrical pull between positive and negative ions. The bond energy is the sum of a molecule's bond dissociation energies.
The phenomenon of the union of two or more atoms involving the redistribution of electrons so that each atom involved in bonding acquires a. A chemical bond is an attraction between atoms. Molecules of chemical substances are joined together by some force.
The chemical bond which is formed by the transfer of electrons between atoms is known as an ionic bond.
The law of conservation of mass states, “the mass in an isolated system can neither be created nor be destroyed but can be transformed from one form to another.” according to. Or the general definition is:

First Law Of Thermodynamics: Law Of Conservation Of Energy - Video & Lesson Transcript | Study.com
This means that a system always has the same.
Law of conservation of energy definition chemistry. Chemistry is a physical science that studies matter, energy and how they interact. When studying these interactions, it's important to understand the law of conservation of. The equation for the law of conservation of energy is:
Although it may be transformed from one form to another. It is also known as the law of conservation of mass. The law of conservation of energy states that energy can neither be created nor destroyed.
For example, when a block slides down a slope, potential energy is converted into kinetic energy. The law of conservation of mass or principle of mass conservation states that for any system closed to all transfers of matter and energy, the mass of the system must remain. In physics the term conservation refers to something which doesnt change.
Conservation of energy definition chemistry. The truly conserved quantity is the sum of kinetic, potential, and thermal energy. The later is used in physics while the former in chemistry.
According to the first law of thermodynamics energy must be conserved, that is, the chemical energy stored in the reactant + the heat energy supplied must equal the amount of chemical. State the law of conservation of mass and energy. The law of conservation of energy states that energy can change from one form into another, but it cannot be created or destroyed.
The law of conservation of matter is a fundamental law in science. E=mc^2 where, e = energy m. The law of conservation of mass and energy describes that the total mass and energy in a closed system remains.
You will also often detect an energy. Also, h x + not only can, but actually does combine with c o x 3 x 2 − to form a new particle:

Chemical Changes Occur During Chemical Reactions. Atoms Rearrange And One Substance Changes Into Another Substance. Reactant = Substance Used In. - Ppt Download
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the chemical transformation of one set of chemical substances to another.

Can a chemical reaction happen with only one substance. Chemical reactions only occur if there is ‘energetics” and “kinetics” that favor it. We can tell if a chemical reaction has taken place when one or more of the following things happen: In a chemical reaction, only the atoms present in the reactants can end up in the products.
Some examples of simple synthesis reactions include: The simple chemical change definition is the changing of one or more substances into another substance(s). A chemical reaction is the process that takes place when a substance (or substances) are brought into contact with each other and produce a new substance (s).
While there certainly are any number of chemical reactions that occur immediately after a. No new atoms are created, and no atoms are destroyed. H c o x 3 x.
The substance(s) to the right of the arrow are called products. For example when water hits chlorine gas it can create. Chemical reactions occur when atoms are.
Can a substance undergo a chemical and nuclear reaction from one cause? In a synthesis reaction, also known as a direct combination reaction, two chemicals (a and b) make a new substance (ab). A chemical reaction is when the bonds are broken within reactant molecules, and new bonds are formed within product molecules to form a new substance.
Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve. This means that a reaction will only go in one direction, from reactants to products, and never the other way around. That movement is an important part of what causes chemical reactions.
There has been a colour change inside the reaction flask. A measure of how easily a substance combines with other substances to produce a. An example of a chemical property is reactivity.
In other types of chemical reactions, gases are evolved, color. Chemical reactions occur all the time, because the molecules in all substances are constantly moving. Chemical changes occur during chemical reactions where chemical.
The key point to remember is fairly easy: There has been a chemical reaction only when one or more new substances are made.sometimes this is obvious, sometimes less so. Some chemical reactions are quite evident, like the burning of gasoline, and involve the production of heat or light.
A reactant is a substance that is present at the start of a chemical reaction. Your example is not quite the case when multiple reactions are possible. Energetics does not refer to a single reactant, but to the “system of reactants” that includes.